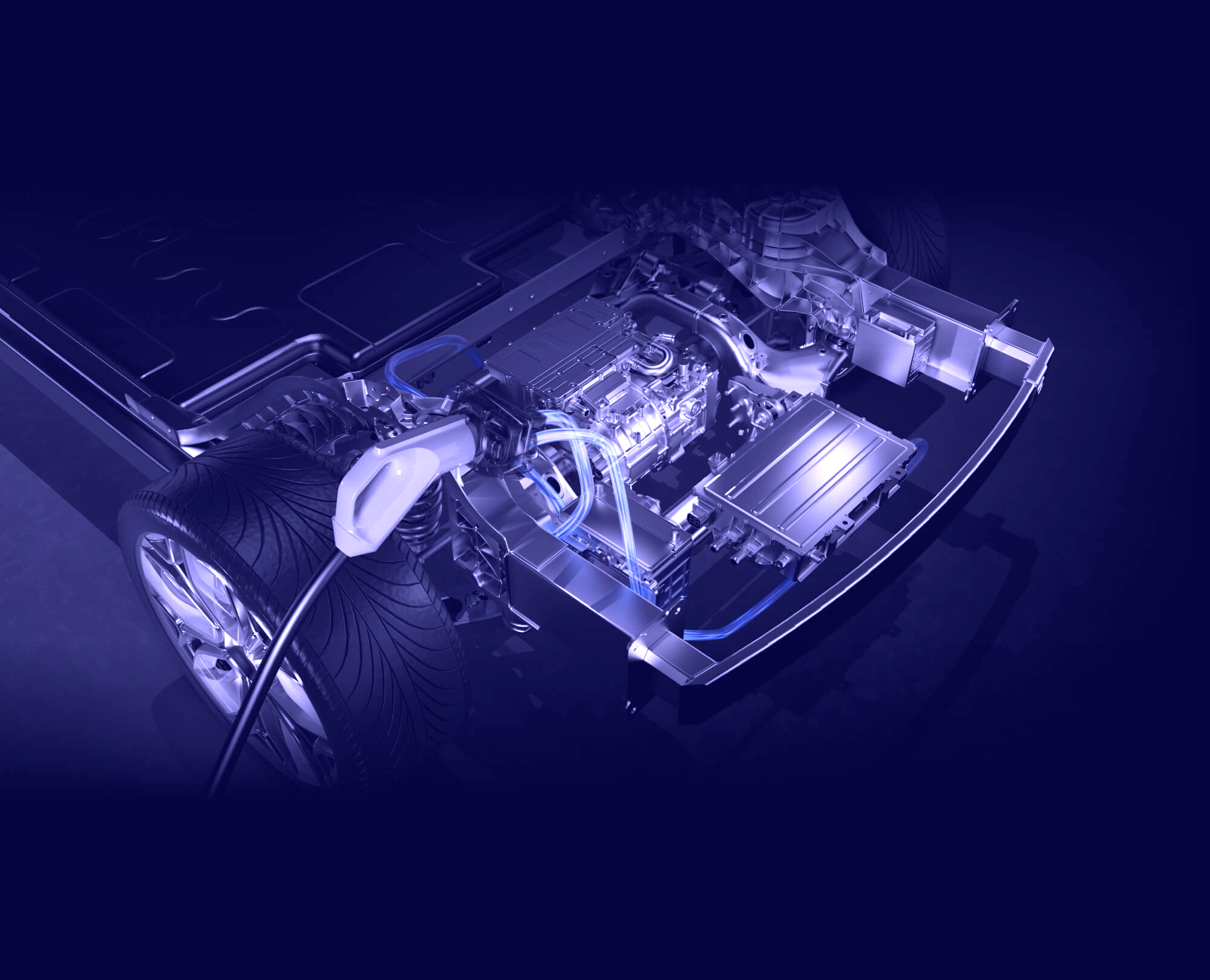
Just like their gasoline counterparts, electric vehicles (EVs) can experience issues that require diagnostics to identify and resolve. However, the nature of these issues and the methods used for diagnosis can differ significantly due to the unique powertrain and electronic systems of EVs. Understanding car diagnostics for electric vehicles is crucial for both EV owners and technicians to ensure optimal performance, safety, and longevity.
Why is Diagnostics Important for Electric Vehicles?
Modern vehicles, including EVs, are equipped with sophisticated onboard computer systems that monitor various aspects of the car’s operation. These systems can detect faults, log error codes, and provide valuable insights into the health and performance of different components. Diagnostics play a vital role in:
- Identifying the root cause of problems: When an issue arises, diagnostics help pinpoint the exact component or system malfunctioning.
- Ensuring safety: Diagnosing and resolving issues related to the high-voltage system, braking, or other critical safety features is paramount.
- Maintaining optimal performance: Identifying and addressing issues early can prevent reduced range, decreased power, or other performance-related problems.
- Preventing further damage: Diagnosing a minor fault can prevent it from causing more significant and costly damage down the line.
- Facilitating efficient repairs: Accurate diagnostics lead to quicker and more effective repairs, saving time and money.
Key Areas of Diagnostics in Electric Vehicles:


While traditional car diagnostics often focus on the engine, transmission, and exhaust systems, EV diagnostics primarily revolve around:
- Battery System: This is arguably the most critical area. Diagnostics for the battery involve assessing its state of charge (SoC), state of health (SoH), cell voltage imbalances, temperature irregularities, and any faults within the battery management system (BMS). Specialized tools and software are required to access this data.
- Electric Motors and Inverters: Diagnosing issues with the electric motors involves checking their performance, temperature, and any unusual noises or vibrations. For the inverters, which convert DC power from the battery to AC power for the motors, diagnostics focus on their operational status and any fault codes.
- Charging System: This includes the onboard charger, charging port, and related circuitry. Diagnostics here involve checking for charging errors, slow charging speeds, or the inability to charge.
- Braking System: While regenerative braking reduces wear, the conventional hydraulic braking system still needs attention. Diagnostics include checking for ABS faults, brake pressure issues, and sensor malfunctions. Additionally, the regenerative braking system itself can have diagnostic codes related to its performance.
- Thermal Management System: As mentioned earlier, temperature regulation is crucial for the battery, motors, and electronics. Diagnostics involve checking coolant levels, pump operation, and identifying any overheating issues.
- Power Electronics: This encompasses various control units and power distribution systems within the EV. Diagnostics here involve reading fault codes and assessing the functionality of these critical components.
- Software and Firmware: EVs rely heavily on software for controlling various functions. Diagnostics may involve checking for software glitches, compatibility issues, or the need for updates.
Tools and Techniques for EV Diagnostics:
Diagnosing electric vehicles often requires specialized tools and software that go beyond generic OBD-II scanners. These include:
- Manufacturer-Specific Diagnostic Tools: These tools provide in-depth access to the EV’s control units and allow for comprehensive diagnostics of the battery, motor, and other unique EV systems.
- Battery Diagnostic Equipment: Specialized equipment can analyze the health and performance of individual battery cells and modules.
- High-Voltage Testing Equipment: Safety is paramount when working with EVs. Insulated multimeters and other high-voltage testing tools are essential for safely diagnosing electrical issues.
- Software and Apps: Some manufacturers provide proprietary software or mobile apps that can interface with the vehicle’s diagnostic systems.
- OBD-II Scanners: While limited in their access to EV-specific systems, standard OBD-II scanners can still retrieve some generic fault codes related to the vehicle’s overall operation.
The Diagnostic Process for EVs:
The diagnostic process for an EV typically involves:
- Customer Interview: Gathering information about the symptoms and when they occur.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for any obvious physical damage or issues.
- Reading Fault Codes: Using specialized diagnostic tools to retrieve error codes from the vehicle’s control units.
- Data Analysis: Interpreting the fault codes and analyzing live data from various sensors and systems.
- Component Testing: Performing specific tests on individual components to verify their functionality.
- System Analysis: Understanding how different systems interact to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
- Formulating a Repair Plan: Based on the diagnostic findings, outlining the necessary repairs.
Car diagnostics for electric vehicles is a critical aspect of ownership and maintenance. Understanding the unique systems and the diagnostic processes involved ensures that any issues can be identified and resolved efficiently, maintaining the safety, performance, and longevity of these innovative vehicles. As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, the importance of skilled technicians and specialized diagnostic tools will only increase.